Business intelligence versus economic intelligence
Let's start this overview by presenting the key definitions. Start by watching this short video.
- Business intelligence
- Decision-support computing, also known as business intelligence (BI), refers to a set of information technology methods, resources and tools used for managing businesses and assisting with decision-making: dashboards, analytical reviews and prospective reports.
Source : Futura Science
- Economic intelligence
- Economic intelligence can be defined as all of the coordinated research, processing and distribution actions carried out with a view to using information that is relevant to economic actors.
Source: Rapport Martre, La Documentation Française, Paris, 1994
Decision-support architectures
It is essential to be aware of the architectures of decision-support information systems (designed to support decision-making) and to understand their differences in relation to operational systems (those designed to support business implementation).
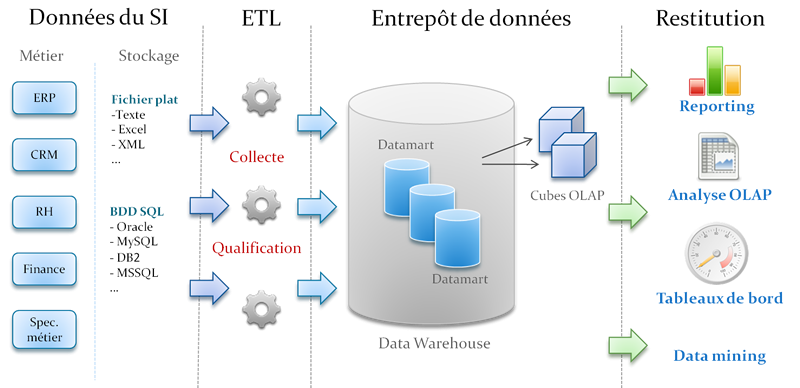
Source : Digicap (consulted on 29 August 2018)
A decision-support information system is populated with data from the operational system but is deployed on a different infrastructure to prevent decision-support issues from interfering with the conduct of business operations.
- The first component is the ETL (Extract, Transform, and Load) zone in which the data processing is carried out.
- The second component is the data storage zone.
- The final component is the data retrieval zone covering all tools used to generate reports or dashboards.
Decision-makers at the heart of the process
Although this field is governed by methods, formalism and best practices, a key aspect of business intelligence is the need to place decision makers at the heart of the process! Not only in order to identify their needs but also to make relevant choices concerning the structuring of data.

The specifications of decision-support systems are based on:
- the decision makers' needs
- the company's business processes
Project management assistance consists in understanding the needs and reformulating them for project management purposes. It is therefore important to be capable of conducting interviews with clients.
Dashboards
Dashboards are the most visible facet of Business Intelligence. Good practices need to be implemented in order to avoid producing illegible compilations of graphics.
Dashboards can meet different kinds of needs, which need to be identified as quickly as possible:
- Strategic dashboards meet the needs of senior management.
- Tactical dashboards meet the needs of heads of teams and departments.
- Operational dashboards meet the needs of different business activities.
When designing a dashboard, you need to ensure compliance with two categories of good practices:
- the accessibility of information.
- the overall coherence of the chosen indicators and their representation.
Dimensional modeling
Modeling data for decision-making is fundamentally different from modeling data for operational systems.
First of all, there is no problem of competing access to data, which is accessible in read-only mode (updates are carried out by means of periodic refreshes which are not impacted by any competition from write mode).
In addition, the queries are often highly complex because they require the filtering and aggregation of data according to different perspectives, whereas in an operational system, information is sought at the atomic level (information about a client, an order, etc.).
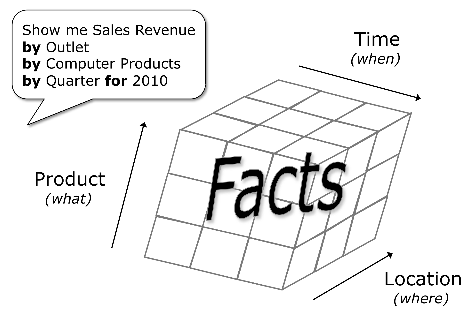
Data cube
We want to be able to observe measures from different observational perspectives: for example, we could consider sales revenue per product, per period, or per location (or even a combination of all three).
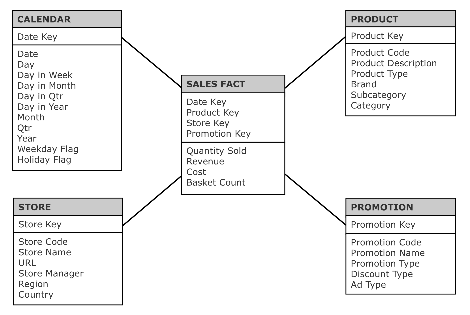
Star schema
In order to generalize the cube concept, data is modeled in the form of star schemas.
Irrespective of the data-storage technology used, dimensional modeling is the most suitable method for consolidating and historizing structural data from which numerous aggregates can be produced to create indicators.
Decision-support project management
Agile approaches are especially appropriate for managing the majority of decision-support projects, which are meant to be responsive to organizational changes and therefore capable of producing usable products within a reasonable time frame. However, it should be noted that in certain situations (particularly in very mature companies at the organizational level), this type of approach may be called into question. In general, agile methods are beneficial because:
- They enable adaptation to changes in users' requirements.
- They increase the engagement of different stakeholders (users, funders, heads of departments, etc.) in the project.
- Kimball's approach is consistent with the methods used for managing agile projects.
The stages of a decision-making project
During each sprint you will have to implement the following steps:
- Define the objectives of each stakeholder.
- Identify functional needs.
- Design (or update) the dimensional diagram.
- Design (or update) dashboards.
- Design ETL processes and test implementation.
Bibliography
Here are four reference books which we recommend as an introduction to this field. Check out the complete bibliography to find out more.




As most of the books are in English, we have also created a glossary containing the translations of certain technical terms.